
Download Our Decision Making Matrix Template Today
Share
Demystifying the Decision Making Matrix

Making important decisions can often feel like navigating a complex maze. A decision making matrix template provides much-needed structure, transforming this potentially overwhelming process into a manageable and logical exercise. Think of these templates as a bridge, effectively connecting your intuitive thinking with data-driven analysis. This allows stakeholders to move beyond gut feelings and make more objective evaluations.
For example, imagine a startup founder grappling with the decision of which market entry strategy to pursue. A decision making matrix enables them to objectively assess each approach, carefully considering key factors such as market size, competition, and available resources.
Understanding the Power of Structure
Decision making matrix templates have gained considerable traction, particularly within business environments. This rise in popularity stems from their structured approach to evaluating options against pre-defined criteria. To fully appreciate the importance of a structured approach, consider a robust strategic decision making framework.
This structured method minimizes the risk of overlooking critical factors in the decision-making process. In fact, studies show that using these templates can increase efficiency and productivity by up to 20%. Furthermore, decision matrices promote transparency and accountability, thereby building trust among stakeholders. Learn more about the benefits of decision matrices here.
Breaking Down the Matrix
The typical decision making matrix template utilizes a table format. Options are listed along one axis, while criteria are listed along the other. Each option is then scored against each criterion, facilitating a clear and direct comparison.
- Options: These represent the different choices under consideration – the potential paths forward.
- Criteria: These are the factors used to evaluate each option, essentially the key elements that influence the final decision.
- Scoring: This involves assigning a numerical or qualitative value to each option based on how well it satisfies the given criteria. This process creates a quantifiable basis for comparison.
Example: Choosing a Project Management Software
Let's say your task is to choose new project management software. Your criteria might include factors like:
- Ease of Use
- Cost
- Integration with Existing Tools
- Collaboration Features
You would then systematically score each software option against these criteria. This process clearly reveals which software best aligns with your specific needs. This structured evaluation process ensures that all relevant factors are considered, ultimately leading to more informed and well-reasoned decisions. It also creates a clear rationale for the final decision, fostering transparency and understanding within the team. This methodical approach helps avoid impulsive choices based solely on first impressions or inherent biases.
Building Your First Matrix: A Step-by-Step Guide

Creating a decision matrix may seem complicated, but the process is surprisingly simple. This guide will help you build your first matrix, transforming complex decisions into manageable, structured choices.
Defining Your Decision and Criteria
The first step is to clearly define the decision you need to make. This provides a crucial foundation for the entire process. Then, identify the relevant criteria for your decision. These criteria are the factors you'll use to evaluate your options, much like evaluating software based on features, usability, and price.
Clearly stating the decision is essential. For example, "Which marketing campaign should we implement next quarter?"
Brainstorming relevant criteria is the next step. Ask yourself which factors influence your decision. These could include potential ROI, cost, and required time commitment.
Structuring Your Matrix
After identifying your criteria, you can structure your decision matrix. This typically involves a table listing your options on one side and your criteria across the top, providing a clear visual representation of the decision-making process.
Create a table. You can use a spreadsheet program, a word processor, or even create one by hand.
List your options. These are the different choices you're evaluating.
Add your criteria as column headers. This format allows easy comparison between options.
To help visualize the structure, consider the following table format:
Basic Decision Matrix Structure
A visual representation of the basic components and format of a decision making matrix.
| Matrix Element | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Options | The different choices being considered | Campaign A, Campaign B, Campaign C |
| Criteria | The factors influencing the decision | Cost, ROI, Time Commitment |
| Scores | The evaluation of each option against each criterion | 1-5, Low/Medium/High |
This table outlines the essential elements within a decision matrix and offers a practical example of how these elements might appear in a real-world scenario. Understanding this structure is crucial for effectively using the matrix to make informed decisions.
Establishing Your Evaluation Parameters
With your matrix structured, define how you'll evaluate each option against each criterion. You can use a numerical scale (e.g., 1-5) or a qualitative assessment (e.g., low, medium, high). This adds objectivity to your decision-making. For team decisions, consider resources like this Scrum Daily Standup Meeting Template.
Choose a scoring system appropriate for your decision's complexity.
Clearly define what each score represents to ensure consistency and clarity.
For example, a "5" for "Cost-Effectiveness" could represent "Extremely Cost-Effective," while a "1" might indicate "Not Cost-Effective."
Populating Your Matrix
Once you've set your criteria and scoring system, begin populating the matrix. Systematically evaluate each option against each criterion, assigning the appropriate score. This methodical approach helps maintain objectivity and ensures all factors are considered. Resources like How to master organization and time management can be beneficial.
Work through each cell methodically. Be as objective as possible in your assessment.
Support your scores with evidence such as data or research whenever possible to bolster credibility.
Analyzing and Making the Decision
After completing your matrix, analyze the results. Which option achieved the highest overall score? Are there clear winners or losers? This analysis provides actionable insights. This data-driven process reduces impulsive choices based on gut feelings. Remember, the matrix informs your decision, but you make the final call.
Based on your analysis, make your decision. The matrix offers a structured framework, but the ultimate choice remains yours. This combines the matrix’s objectivity with your understanding of the situation.
Weighted Decision Matrices: Beyond Basic Comparisons
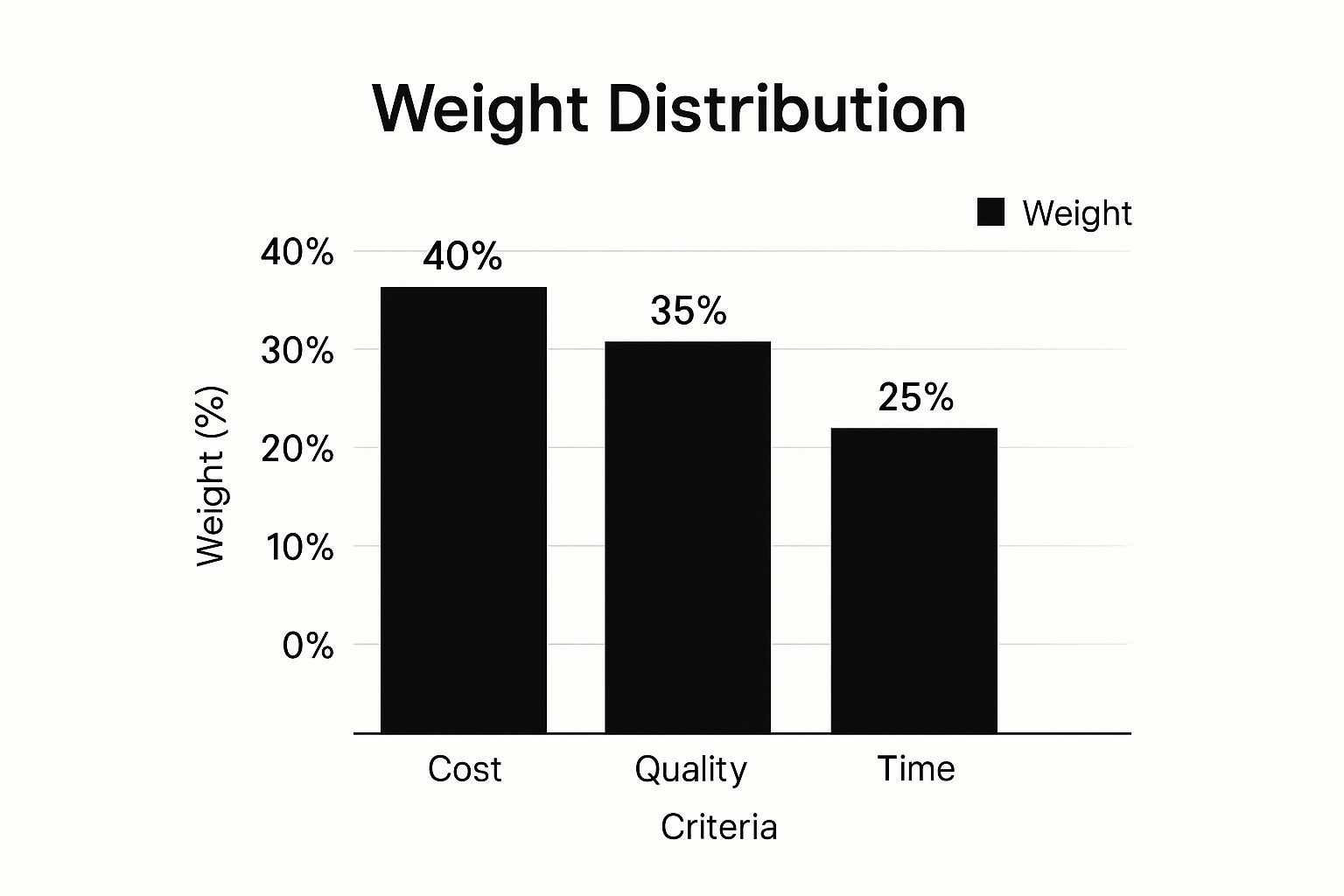
The infographic above illustrates how weights are distributed across criteria. In this example, Cost (40%), Quality (35%), and Time (25%) are the key factors. Cost is the most heavily weighted, closely followed by Quality. Time is the least important factor in this particular decision-making matrix. This weighting system emphasizes how you can prioritize specific criteria based on their importance to the final decision.
While basic decision matrices are useful, they assume all criteria are equally important. In real-world scenarios, this is rarely true. This is why weighted decision matrices are so valuable. They allow you to assign different weights, reflecting the relative importance of each criterion. This transforms the matrix from a simple comparison into a robust decision-making tool.
Understanding Weights and Their Impact
Weighting adds a crucial layer of depth to decision-making. Imagine choosing a new office. While proximity to public transport matters, it's probably less important than the rental cost. A weighted matrix allows you to quantify this difference.
You could assign weights of 30% to cost, 20% to transport, and 50% to office size, aligning with your priorities. This establishes a hierarchy of importance, ensuring the most critical factors have the biggest impact. For more on effective decision-making, check out this resource: How to master effective decision-making techniques.
Assigning Meaningful Weights: Moving Beyond Arbitrary Percentages
Assigning weights isn't about randomly selecting percentages. It requires careful consideration of each criterion's contribution to your overall objective. Pairwise comparison is a helpful technique, directly comparing each criterion to every other to determine relative importance. This forces you to consider trade-offs, leading to a more accurate weighting system.
Including multiple stakeholders is also beneficial. Diverse perspectives can reveal potential biases and provide a more comprehensive understanding of the decision's complexities. Weighted decision matrices are used across diverse industries, ensuring decisions are both logical and transparent. Learn more about their power here.
Validating Your Weighting System and Conducting Sensitivity Analysis
After assigning weights, validate them against unconscious biases. Critically examine the weights to ensure they genuinely reflect the decision’s objectives and aren't influenced by preconceived notions.
Sensitivity analysis is also crucial. This involves adjusting the weights to see how they influence the outcome. This tests the decision's robustness under various scenarios, providing insights into potential risks and rewards associated with each option. By incorporating weights and sensitivity analysis, you gain deeper understanding and confidence in your final decision.
To illustrate, let's consider a Weighted Decision Matrix Example:
A comparison of different product options is evaluated using a weighted decision matrix shown below. This matrix helps to visualize how different scores and weights contribute to the final weighted scores for each option.
| Criteria | Weight | Option A Score | Option A Weighted | Option B Score | Option B Weighted | Option C Score | Option C Weighted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feature Set | 25% | 8 | 2 | 9 | 2.25 | 7 | 1.75 |
| Cost | 40% | 7 | 2.8 | 6 | 2.4 | 9 | 3.6 |
| User Friendliness | 35% | 9 | 3.15 | 7 | 2.45 | 8 | 2.8 |
| Total Weighted Score | 7.95 | 7.1 | 8.15 |
This weighted decision matrix example demonstrates how Option C emerges as the preferred choice despite not having the highest score in any individual criterion. Its strong performance in Cost and User Friendliness, combined with the assigned weights, contribute to its higher overall weighted score. This example shows how a weighted decision matrix can lead to a more balanced and informed choice.
Transforming Group Decisions From Chaos to Consensus

Group decisions can often be challenging. Competing opinions and dominant personalities can create a confusing and unproductive environment. However, decision making matrix templates provide a structured approach that promotes fairness and transparency. These templates shift the focus from subjective opinions to objective evaluations, helping teams reach a consensus more efficiently.
Facilitating Matrix-Driven Discussions
Consider a cross-functional team selecting a new marketing campaign. A decision making matrix template creates a shared framework. It gives every team member an equal opportunity to contribute and participate in the process. This structure helps guide discussions, keeping them focused on pre-defined criteria.
Instead of simply advocating for their preferred campaign, team members objectively evaluate each option. Factors like budget, target audience, and potential ROI become the focus. This collaborative, objective approach encourages thoughtful evaluation and minimizes the impact of personal biases.
Leveraging Digital Collaboration Platforms
Digital platforms significantly enhance the power of decision making matrix templates in collaborative work. Platforms like Miro offer templates such as the weighted decision matrix and the Eisenhower matrix. These tools simplify the decision-making process. Teams can easily define criteria, assign weights, and evaluate options together. This collaborative approach can improve team productivity by up to 25% by ensuring everyone feels valued and aligned. Decision matrices can also be used in real-time during meetings to capture all relevant information. Explore these decision matrix templates here. You can also find more information on organization and time management here.
Managing Conflicting Viewpoints and Building Alignment
Even with a structured matrix, disagreements are bound to happen. Successfully navigating these conflicts is key to achieving true consensus. Facilitators should promote open discussion, ensuring everyone feels comfortable sharing their perspectives and concerns.
Techniques like active listening and constructive feedback can help manage conflicting viewpoints effectively. The goal is not to eliminate disagreement, but to use it constructively. The decision matrix serves as a tool to find common ground and build consensus. This collaborative approach fosters team alignment. The final decision will then have genuine support, rather than just reluctant acceptance. This results in a decision that truly reflects the collective wisdom of the group.
Specialized Matrices For Every Decision Scenario
A standard decision making matrix template offers a valuable framework. However, its true strength lies in its adaptability. Decisions vary, and so should the tools we use to make them. This section explores how professionals tailor these matrices for specific scenarios, capturing the nuances of each unique decision context.
Procurement: Vendor Selection
Procurement teams frequently navigate the complex process of vendor selection. A specialized decision making matrix template can simplify this. Standard criteria often include price, quality, delivery time, and past performance. However, specific product or service requirements may necessitate additional criteria like vendor sustainability or technological capabilities.
For instance, choosing a software vendor often requires considering security certifications and integration capabilities. This ensures the vendor aligns with the organization's long-term IT strategy.
Product Management: Feature Prioritization
Product managers constantly balance competing priorities when determining which features to develop. A specialized decision making matrix template helps prioritize based on factors like user value, development cost, and market demand. This focus allows product teams to deliver maximum impact and user satisfaction.
Consider a mobile app development team. Key criteria might include user engagement metrics, development feasibility, and alignment with the overall app vision.
Human Resources: Candidate Assessment
Effective hiring is crucial for organizational success. A specialized decision making matrix template helps hiring committees objectively evaluate candidates based on skills, experience, cultural fit, and other relevant factors. This structured approach minimizes bias and ensures candidate alignment with job requirements and team dynamics.
When hiring for leadership positions, criteria like communication skills, strategic thinking, and leadership experience become particularly important. This targeted approach improves the likelihood of selecting successful leaders.
Investment: Portfolio Evaluation
Investors often use a specialized decision making matrix template to assess their portfolios. Factors such as potential return, risk level, market trends, and diversification are crucial in this evaluation. This methodical approach helps investors make informed decisions aligned with their risk tolerance and investment goals.
A real estate investor, for example, might consider factors like property location, rental income potential, and property appreciation when evaluating an investment opportunity. You might be interested in: How to master project organization and time management.
Adapting Templates To Your Unique Context
The key takeaway is adapting the decision making matrix template to your specific circumstances. While the core structure remains constant, criteria and weighting should reflect the unique demands of each situation.
This involves thoughtfully considering the factors influencing your decision and assigning appropriate weights based on their relative importance. This personalized approach ensures your matrix remains a powerful tool for making informed and effective decisions. Understanding these specialized applications unlocks the full potential of decision making matrices for better outcomes in all areas of your work and personal life.
Avoiding Matrix Missteps: Common Pitfalls and Solutions
Decision-making matrix templates are powerful tools for evaluating options and making informed choices. However, like any tool, they can be misused. Understanding potential pitfalls helps ensure your matrix delivers reliable results and leads to sound decisions.
Confirmation Bias: Seeing What You Want To See
One common pitfall is confirmation bias. This occurs when we unconsciously favor information that confirms pre-existing beliefs. It can skew scoring within the matrix, leading to decisions based on subjective preferences rather than objective evaluation. For example, if you already lean towards Option A, you might unconsciously assign it higher scores, even if the evidence doesn't fully support this assessment.
Combating confirmation bias requires conscious effort. Actively seek out information that challenges your initial inclinations. Consider incorporating diverse perspectives to gain a more balanced and objective view of the available options.
Criteria Overlap: Double-Counting for Inflated Scores
Another potential misstep is criteria overlap. This happens when multiple criteria within the matrix measure the same underlying factor. Such overlap leads to unintentional double-counting, artificially inflating scores and distorting the true comparison between options. For instance, criteria like "User Friendliness" and "Ease of Use" might overlap significantly.
To avoid this issue, carefully define each criterion within your matrix. Ensure each one measures a distinct aspect of the decision at hand. If two or more criteria seem very similar, consider combining them into a single, more comprehensive measure.
Inconsistent Evaluation Standards: Apples and Oranges
Inconsistency in applying evaluation standards can also undermine the validity of a decision matrix. If your scoring criteria fluctuate throughout the evaluation process, the comparison becomes meaningless, much like comparing apples and oranges.
To prevent this, establish clear definitions for each score or rating level used in your matrix. Document the rationale behind each score assigned to maintain transparency and consistency. This structured approach ensures a fair comparison and leads to more robust decision-making. You might be interested in: How to master project organization and time management.
Validating Your Matrix: Ensuring Accurate Insights
Detecting questionable results requires critical evaluation. If the outcome of your matrix seems counterintuitive or contradicts other available evidence, it's essential to re-examine the matrix itself. Carefully review the chosen criteria, their assigned weights (if used), and the individual scores. Look for potential biases, overlaps, or inconsistencies. This careful review ensures your decision-making tool is producing reliable and accurate insights.
Correcting Course: Practical Solutions for Matrix Missteps
Correcting identified issues often involves refining criteria, re-evaluating scores, or adjusting weights. Documenting these changes maintains transparency and provides valuable lessons for future decision-making processes. In some cases, completely revisiting the entire matrix process might be necessary to ensure accuracy.
Real-World Example: A Project Gone Wrong (and Right)
A team tasked with selecting project management software initially overemphasized "Features" while underweighting "Cost." This led them to select a powerful but overly expensive option that strained their budget. Realizing their mistake, the team revised the decision matrix, increasing the weight assigned to "Cost." This resulted in choosing a more affordable software option that still met their core needs. This example demonstrates how correcting a flawed matrix can lead to a more practical and successful outcome. By understanding and addressing these common pitfalls, you can transform your decision-making matrix template into a reliable tool for clear, effective, and unbiased decision-making.
Creating a Matrix-Driven Decision Culture
Building a decision-making culture based on matrices involves more than simply understanding how to create a decision making matrix template. It requires weaving this valuable tool into the core of your team's operational processes. This represents a fundamental shift in mindset, not just the adoption of a new tool.
Fostering Buy-In and Training
Introducing any new process can be met with resistance. Some team members, particularly those used to intuitive decision-making, may be skeptical of structured approaches. Addressing these concerns directly is essential for successful implementation. Begin by illustrating the advantages of decision making matrix templates with practical examples. Showing how these templates result in clearer, more justifiable decisions can help convince those who are hesitant.
Furthermore, provide comprehensive training on how to use the templates effectively. This training should cover not just the technical steps of creating a matrix, but also the core principles of objective assessment and criteria selection. This empowers team members to use matrices confidently in their daily work.
Integrating Matrices Into Existing Workflows
For long-term adoption, seamless integration is key. Instead of forcing matrices into current workflows, explore how they can enhance existing processes. For example, a decision matrix can be a valuable asset in project retrospectives, providing a structured method for evaluating project outcomes and pinpointing areas for improvement.
This integration can be further strengthened by using collaborative platforms like Miro. Miro offers various decision making matrix templates specifically for team collaboration. These platforms create a central hub for teams to work together on matrices, fostering discussion and consensus.
Documenting Decisions for Continuous Improvement
Documenting decisions made with matrices builds a valuable knowledge base. This documentation serves as a record of the logic behind previous decisions, providing useful insights for future choices. This historical context also offers a benchmark for assessing the effectiveness of matrix-driven decisions. By analyzing the results of these decisions, teams can refine their criteria selection and weighting, driving ongoing improvement in the decision-making process. This iterative approach helps optimize the use of matrices over time, ensuring they remain relevant and impactful.
Measuring the Impact of Matrix-Based Decisions
Showing the tangible benefits of matrix-driven decisions is critical for maintaining buy-in. This involves establishing clear metrics to evaluate the impact of these decisions on business outcomes. These metrics could include faster project delivery times, cost reductions, or higher customer satisfaction.
By tracking these metrics, teams can clearly show the value of using decision making matrix templates. This data-driven approach not only justifies the continued use of matrices but also highlights opportunities for further optimization. Ultimately, this emphasis on measurable results reinforces the role of matrices as an integral part of a successful decision-making culture.
Ready to enhance your decision-making process? The Boss Personal Planner provides the structure and tools you need to transform decisions into action and achieve your goals. Visit Boss Personal Planner today and start planning your path to success!
